
On the flip side, a lower multiplier might suggest a safer bet, with the company being less burdened by debt. Benchmarking your company’s equity multiplier against the industry average ensures your capital structure aligns with market norms. If a different company’s assets are $825 billion with $165 billion of shareholders’ equity, the same resulting ratio is 5X ($825 / $165). The company in our illustrative example has an equity multiplier of 2.0x, so the $1.35m assets on its balance sheet were funded equally between debt and equity, with each contributing $675k. The equity multiplier is one of the ratios that make up the DuPont analysis, which is a framework to calculate the return on equity (ROE) of companies. The Equity Multiplier ratio measures the proportion of a company’s assets funded by its equity shareholders as opposed to debt providers.
It helps with investor or lender risk assessment
It’s a bit like trying to read a map while spinning around—disorienting to say the least. In simple terms, a higher equity multiplier can amplify ROE—but it also means taking on more debt-related risk. To calculate the shareholders’ equity account, our model assumes that the only liabilities are the total debt, so the equity is equal to total assets subtracted by total debt. Let us now consider the same example to check how to use the equity multiplier formula in Excel with the two inputs – Total Assets and Equity Multiplier. Here, the available details help calculate the equity multiplier ratio easily in the template provided. Apple, an established and successful blue-chip company, enjoys less leverage and can comfortably service its debts.
Strategy Roadmaps
- In the case of Company C, an automotive manufacturer, the equity multiplier has steadily increased over the past five years.
- Equity multiplier can also compare the financial structure of different companies.
- Because it suggests the company isn’t overly reliant on debt to finance its assets.
- Lower is generally safer but may indicate underutilized leverage opportunities.
- The equity multiplier is a financial ratio that measures a company’s financial leverage by comparing its total assets to shareholders’ equity.
- The ratio of the two helps investors assess the financial leverage of a company, allowing them to make better investment decisions.
With the numbers for total assets and shareholders’ equity, simply divide the total assets by the shareholders’ equity. We will follow the equity multiplier formula and will put the data we have into the formula to find out the ratios. This is an essential equity multiplier formula consideration since financial leverage would be higher/ lower depending on the equity multiplier calculation (whether the multiplier is higher or lower).

Key Takeaways
Equity multiplier is a financial ratio that measures the amount of the company’s assets that are financed by shareholders’ equity. In conclusion, the equity multiplier is a vital metric for understanding a company’s leverage and its impact on return on equity. By analyzing the equity multiplier, investors and analysts can gain insights into a company’s capital structure, risk profile, and profitability. It’s essential to consider both the equity multiplier and ROE together to form Foreign Currency Translation a comprehensive assessment of a company’s financial health.
Avid investors keep a keen track on the key performance indicators of a company which help them in decision-making. The equity multiplier provides important insights into a company’s financial leverage and risk exposure. As discussed throughout this article, the multiplier measures how much assets a company has acquired through taking on debt. With a shareholders’ equity of $186 billion and total assets of $354 billion, Exxon Mobil has an equity multiplier of 1.9x.
- This post will clearly explain the equity multiplier formula, its meaning, and how to strategically use it to evaluate financial risk and return.
- The term “sweat equity” comes from the idea that you’re investing your “sweat” (labor and effort) instead of money.
- When a firm’s assets are primarily funded by debt, the firm is considered to be highly leveraged and more risky for investors and creditors.
- A high equity multiplier implies that a company mostly uses debt financing to purchase assets, while a low equity multiplier suggests it relies more on equity.
- This example shows how to calculate and understand the equity multiplier using a real-world SaaS company.
- Different industries may have varying levels of leverage that are considered acceptable.
- Equity multiplier formula illustrated as total assets divided by shareholders’ equity.
External perspective: financial leverage from the experts
In simple terms, the equity multiplier indicates how much of a company’s assets are funded by debt compared to equity. A higher equity multiplier ratio indicates that a larger portion of the company’s assets are financed by debt, implying greater financial risk. It’s also indicative of a potentially higher return on equity, subject to the caveat http://shopzyre.com/bookkeeping/how-much-does-a-cpa-cost-certified-public-3/ that the company can manage its debts and financial obligations well.
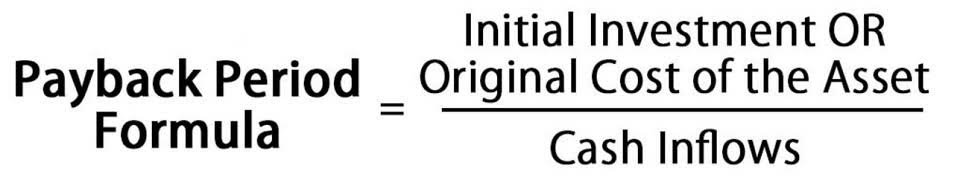
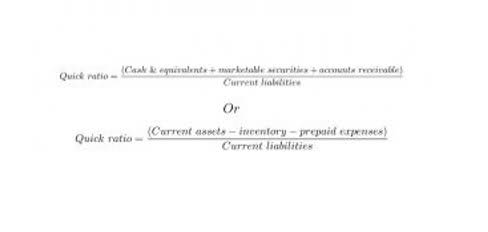
A higher equity multiplier suggests a company is more leveraged, potentially indicating a higher risk profile. Conversely, a lower equity multiplier may indicate a more conservative approach to financing and a lower risk profile. By comparing equity multipliers, investors can evaluate the relative risk and stability of different companies within an industry. Total assets mean all current assets (debtors, inventories, prepaid expenses, etc.) and non-current assets (building, machinery, plants, furniture, etc) of the company’s balance sheet. This is important to note that preference shares would not be part of this because of the nature of the fixed obligation.
Growth stage
If business operations are good, the company’s financial leverage will also be good. The DuPont Analysis tells investors how well a firm is doing with respect to its Return on Equity. The equity multiplier ratio in the DuPont analysis stands for financial leverage that a firm displays in managing its finances. The asset turnover stands for asset use efficiency while the net profit margin tells the investor about the operating efficiency of the firm. Together, these ratios show how dependent a company is on debt financing versus equity financing. A high equity multiplier and debt ratio indicates heavy reliance on debt, raising financial risk.

Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *